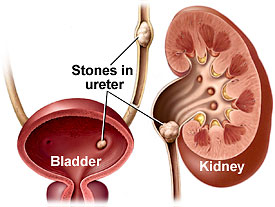
Bladder Stones
Bladder Stones are usually small masses of minerals that form in your bladder. Bladder stones develop when urine in your bladder becomes concentrated, causing minerals in your urine to crystallize. Concentrated, stagnant urine is often the result of not being able to completely empty your bladder. When symptoms do occur, they can range from abdominal pain to blood in your urine.
Small bladder stones sometimes pass on their own, but you may need to have others removed by your doctor. Left untreated, bladder stones can cause infections and other complications.
Visit Our Website For More Information. http://www.drugstoreonline1.com